Oct 21, 2021 By Team YoungWonks *
Kevin Ashton and the Birth of IoT
The term Internet of Things (IoT) was coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999, envisioning a world where physical objects could communicate via the internet using technologies like RFID. This groundbreaking concept has developed into an intricate ecosystem of connected devices, which now include smartphones, smart objects, industrial machines, and home appliances. These IoT devices are part of a vast network that leverages internet connectivity to exchange and process data autonomously.
IoT is powered by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), which enable data analytics to provide deeper insights and drive decision-making. Today, IoT isn't just about connectivity; it’s about enhancing the functionality of devices through intelligent automation. As devices become more autonomous, they can collect data, learn from their environments, and act accordingly without human intervention. This convergence of IoT and AI has led to significant shifts in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation, paving the way for low-power devices that operate efficiently for longer periods. For example, Amazon uses IoT sensors and automation across its logistics network, ensuring timely delivery and improving inventory management, revolutionizing the way the supply chain functions.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?

The IoT refers to a network of connected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet. These devices range from household items like smartphones, thermostats, and refrigerators to complex industrial machines. Through internet connectivity, these objects share data across networks and collect data to optimize their operations, often using AI to process and act on this information.
In essence, IoT solutions make the world around us more intelligent and responsive. Whether it’s smart homes with automated lighting and security systems or factories leveraging IoT deployments for predictive maintenance, the common thread is how IoT technology transforms static objects into dynamic, interconnected systems. For example, a smart thermostat can adjust the temperature based on your daily routine, while smartphones act as hubs to control various other IoT devices in your home. The fusion of AI, data analytics, and low-power IoT devices ensures that these systems work efficiently and intelligently with minimal human input.
For younger learners interested in developing skills for IoT projects, consider enrolling in our Python Coding Classes for Kids to gain foundational programming knowledge.
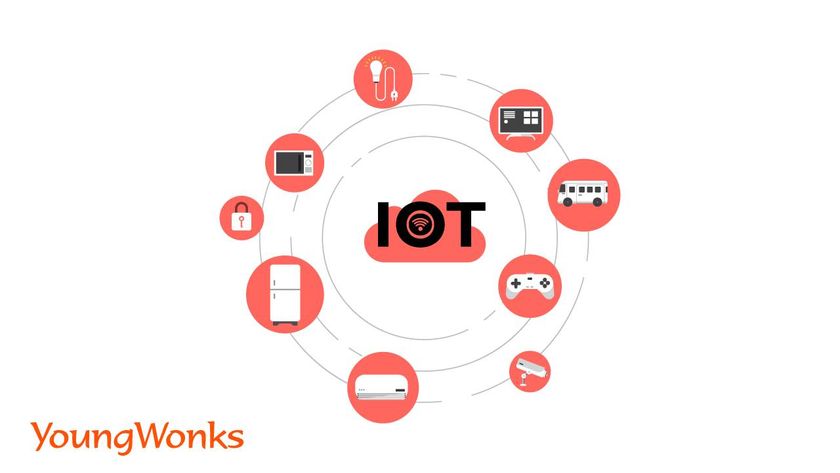
How IoT Works: The Basics
IoT devices consist of four core elements:
- Connected devices: These physical objects are embedded with sensors that allow them to monitor and control certain aspects of the environment. Examples include smart devices, smartwatches and industrial equipment.
- Connectivity: Through internet connectivity, these devices communicate with each other, often using wireless networks like wi-fi, Bluetooth, and routers.
- Data Processing: The data collected by IoT systems is analyzed through data analytics platforms, often in real-time, and this is where artificial intelligence plays a vital role. Companies like Microsoft are pioneers in providing the infrastructure needed for handling the vast amounts of data generated by IoT systems.
- User Interface: Users can interact with IoT systems via smartphones or other digital interfaces, allowing them to monitor or control smart objects with ease.
By leveraging AI and low-power technologies, modern IoT systems are not only more efficient but also more sustainable. These advancements ensure that devices function over extended periods without frequent power-ups, reducing energy consumption—a critical factor in many IoT deployments.
Applications of IoT
IoT has revolutionized multiple sectors by enabling seamless connectivity, automation, and data-driven decision-making. Below are some key applications of IoT and how they are transforming industries and everyday life.
IoT for Smart Homes
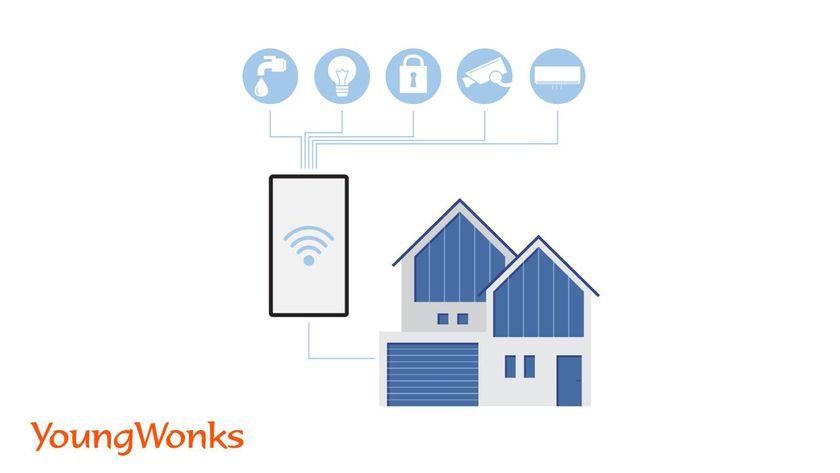
The rise of IoT for smart homes has transformed the way we interact with our living spaces. Smart devices such as thermostats, lighting systems, security cameras, and home assistants like Amazon’s Alexa are all interconnected to create an intelligent, responsive environment. These devices not only provide comfort and convenience but also play a crucial role in building the foundation for smart cities, where homes contribute to a larger, interconnected urban ecosystem.
For instance, smart thermostats learn your daily habits and adjust the home temperature accordingly, reducing energy waste and lowering utility bills. IoT sensors can also detect when no one is home and automatically shut off lights or adjust heating and cooling systems, further enhancing energy efficiency. Smart home ecosystems such as Apple HomeKit and Amazon Echo create a seamless interface for users to control multiple devices through voice commands or mobile apps, enhancing comfort and convenience. This integration of smart homes into broader urban planning paves the way for smart cities that prioritize sustainability, connectivity, and efficient resource management.
Example: A family in a smart home uses their smartphone to lock doors, turn off lights, and adjust their smart thermostat remotely when they leave for vacation, ensuring security and energy efficiency while they’re away.
IoT in Self-driven Vehicles

IoT in self-driven vehicles represents one of the most exciting advancements in transportation. Autonomous vehicles rely on IoT sensors to collect data from their surroundings, enabling them to make real-time decisions, avoid obstacles, and navigate safely without human intervention.
These vehicles are equipped with artificial intelligence, edge computing, and real-time data analytics, which allow them to process information quickly and adapt to dynamic driving conditions. IoT plays a crucial role in connecting these vehicles to traffic management systems, enabling them to communicate with traffic lights, other vehicles, and even pedestrians.
Example: Tesla’s self-driving cars use an array of IoT sensors, cameras, and radar systems to analyze their surroundings. They collect real-time data to navigate highways, detect obstacles, and even park autonomously, offering a glimpse into the future of transportation.
Check out more on deep learning and its role in developing autonomous technologies like self-driving vehicles at the following links: How Does Autonomous Driving Work?, and Self-Driving Cars: What Autonomous Driving Technology Can Do Today
IoT in Retail Shops

IoT in retail shops has dramatically improved the customer experience and operational efficiency. Retailers use smart devices and IoT sensors to track inventory in real time, manage supply chains, and create personalized shopping experiences.
In brick-and-mortar stores, IoT enables smart shelves equipped with weight sensors that notify store managers when stock is low. Retailers like Amazon have taken this a step further with the introduction of cashier-less stores, where customers can pick up items and leave without checking out manually. Sensors track the items taken, and the cost is automatically deducted from their account.
Example: Amazon Go stores use IoT sensors to track customer movements, products picked, and payment, eliminating the need for cashiers. This real-world application of IoT simplifies the shopping experience and improves operational efficiency.
IoT in Wearables

IoT in wearables has gained significant popularity, particularly in the health and fitness sectors. Wearable devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers collect data on users’ physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
These devices use IoT sensors to monitor vital health metrics and send real-time data to cloud platforms or smartphones for analysis. IoT-powered wearables provide users with personalized feedback on their health and fitness, helping them maintain healthier lifestyles. In some cases, wearables can alert users or healthcare providers of irregularities, such as abnormal heart rates, allowing for proactive medical intervention.
Example: The Apple Watch is a popular IoT application in wearables that tracks fitness metrics, monitors heart rate, and even detects falls. It can alert emergency services in the event of a medical emergency, providing life-saving interventions for users.
IoT in Smart Grids

IoT in smart grids has revolutionized the energy sector by creating more efficient and sustainable power distribution systems. Traditional power grids are being replaced by IoT-enabled smart grids, which utilize IoT sensors to monitor energy consumption in real time and adjust power distribution accordingly.
Smart meters installed in homes and businesses allow utility companies to track energy usage and manage demand more efficiently. By optimizing energy flow and reducing waste, smart grids help reduce costs for both providers and consumers. They also integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid more effectively.
Example: Cities like Amsterdam have implemented IoT-based smart grids that monitor energy usage across the city and distribute power more efficiently. This has led to a significant reduction in energy waste and improved integration of renewable energy sources into the grid.
IoT in Farming

IoT in farming, often referred to as smart agriculture, has transformed traditional farming practices by using connected devices to optimize crop production, monitor soil conditions, and manage livestock.
IoT-enabled sensors can monitor soil moisture levels, temperature, and nutrient content in real time, allowing farmers to adjust irrigation and fertilization schedules for maximum crop yield. Drones equipped with IoT technology can survey large fields, monitor plant health, and even apply fertilizers or pesticides with precision. Livestock monitoring devices can track the health and location of animals, ensuring timely care and reducing the loss of livestock.
Example: John Deere, a leading agricultural equipment manufacturer, uses IoT-enabled machinery that can monitor soil conditions, track planting progress, and ensure crops receive the right amount of water and nutrients, optimizing farm productivity
Industrial Internet of Things/ Industrial IoT

The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a subset of IoT focused on connecting industrial machinery, equipment, and systems to enhance manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain management. By integrating IoT sensors into industrial equipment, companies can monitor machinery in real time, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency.
IIoT enables real-time monitoring of production lines, reducing downtime and preventing costly machinery failures. By using edge computing, data can be processed on-site, allowing manufacturers to make real-time adjustments to production processes, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Example: General Electric (GE) uses IIoT applications in its factories to monitor the performance of jet engines during production. The data collected allows for predictive maintenance, reducing equipment downtime and improving overall efficiency.
IoT for Smart Supply-chain Management
IoT for smart supply-chain management is revolutionizing logistics by enabling real-time tracking and automation of various supply chain processes. IoT sensors installed on shipping containers, trucks, and even individual packages can monitor the location, temperature, and condition of goods as they move through the supply chain.
This real-time data helps businesses like Amazon optimize their logistics, reducing delays and improving efficiency. IoT also allows companies to automate warehouse operations, reducing human error and increasing accuracy in inventory management.
Example: DHL uses IoT-enabled supply chains to track shipments and monitor the condition of goods in real time. This ensures that perishable items like food or pharmaceuticals are transported under optimal conditions, reducing waste and ensuring timely delivery.
IoT for Telehealth

IoT for telehealth is transforming healthcare by enabling remote monitoring of patients, real-time data collection, and seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers. IoT devices, such as smartwatches and wearable health trackers, collect data on vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely.
Patients can consult with doctors via telehealth platforms, and the data collected by IoT devices is shared in real time, allowing for quick diagnosis and treatment. IoT also enables remote surgeries, where doctors can operate on patients located miles away using IoT-connected robotic systems.
Example: The Withing’s smart health device ecosystem allows patients to monitor their blood pressure, weight, and heart rate. This data is automatically shared with their healthcare provider, ensuring real-time insights into the patient’s health and enabling timely interventions without the need for in-person visits.
Advantages of IoT
The advantages of IoT are numerous:
- Real-time monitoring: IoT systems collect data and provide actionable insights in real-time, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making.
- Improved functionality: With AI integration, IoT devices offer improved functionality through automation, making processes more efficient.
- Enhanced convenience: From smart homes to self-driving cars, IoT improves our daily lives by automating routine tasks and providing seamless interactions between smart objects.
- Energy efficiency: Low-power devices, such as those used in industrial IoT, reduce energy consumption while ensuring efficient performance.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is reshaping the world, providing innovative IoT solutions that bridge the gap between physical objects and the digital world. With the power of AI, data analytics, and internet connectivity, IoT devices offer new levels of automation, efficiency, and intelligence in everything from smart homes to industrial IoT systems. However, as the number of connected devices grows, so do the challenges related to IoT security.
As companies like Apple, Amazon and Microsoft push the boundaries of IoT, their initiatives and investments in this space will continue to fuel the growth of this transformative technology. The business models emerging from IoT deployments will pave the way for a more connected and automated future, where real-world insights and digital transformation are key drivers of success.
Understanding the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a significant leap forward in our ability to manage, interact with, and understand the devices and systems that make up our daily lives. At the heart of this digital revolution are the programming skills required to create and control these sophisticated networks. By enrolling in Coding Classes for Kids, young learners can start their journey toward mastering these essential skills early on. Our Python Coding Classes for Kids specifically cater to the foundational programming knowledge needed to contribute to IoT projects. Furthermore, for those fascinated by hands-on technology and eager to learn about the hardware aspect of IoT, our Raspberry Pi, Arduino and Game Development Coding Classes offer a deep dive into creating real-world applications and devices, showcasing how software and hardware can work seamlessly together to power the IoT ecosystem.
*Contributors: Written by Disha N; Lead image by: Leonel Cruz