Dec 30, 2021 By Team YoungWonks *
What is an infrared sensor? In a previous blog post (https://www.youngwonks.com/blog/What-is-a-sensor), we briefly looked at the different types of sensors. In this blog post, we shall focus on one of them - the infrared sensor. So what is an infrared sensor, how does it work, where is it used and what are its advantages and disadvantages? Read on to know more…
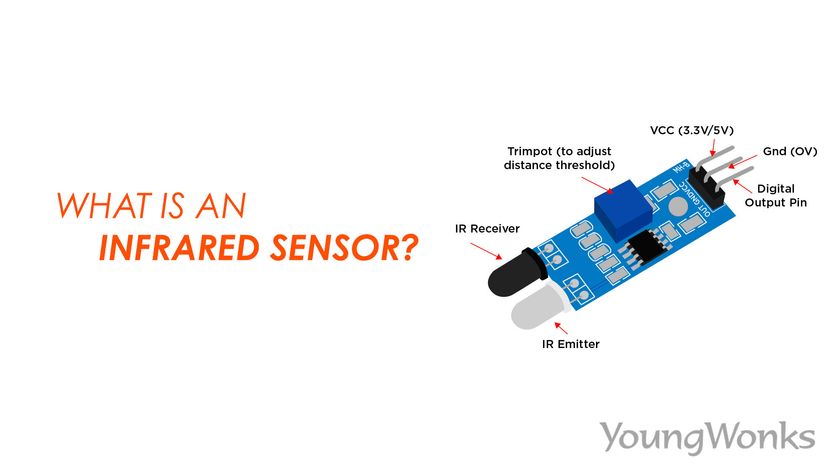
What is an infrared sensor?
An infrared (IR) sensor is an electronic device used to measure and detect infrared radiation in its surrounding environment. What then is infrared radiation? Infrared radiation - also known as infrared light - refers to electromagnetic radiation that has wavelengths longer than those of visible light. In fact, it is said to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter to around 700 nanometers (the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum). It is thus invisible to the human eye but can be detected as a sensation of warmth on the skin.
Infrared radiation (IR) was accidentally discovered by the astronomer William Herschel in the year 1800. As he calculated the temperature of each color of light (separated by a prism), Herschel observed that the temperature just beyond the red light was highest. It is important to note that although the infrared wavelength is longer than that of visible light, it is very much on the same electromagnetic spectrum. Anything that sends out heat - basically has a temperature above around five degrees Kelvin - gives off infrared radiation.
Types of IR sensors
There are two types of infrared sensors: active IR sensors and passive IR sensors.
Active infrared sensors
Active infrared sensors emit and detect infrared radiation. They have two parts: there’s a light emitting diode (LED) and a receiver. When an object comes close to the sensor, the infrared light from the LED bounces off of the object and is detected by the receiver. Active IR sensors thus behave as proximity sensors, and are commonly used in obstacle detection systems such as robots.
Passive infrared sensors
Passive infrared sensors, on the other hand, only detect infrared radiation; they do not emit it from an LED. Passive infrared sensors (PIR) are made up of the following components: two strips of pyroelectric material (a pyroelectric sensor); an infrared filter to block out all other wavelengths of light; a fresnel lens that collects light from several angles into a single point; and a housing unit to protect the sensor from other environmental variables, such as temperature and humidity. PIR sensors are mainly used in PIR-based motion detectors.
How does an infrared sensor work?
An infrared sensor works the same way an object detection sensor does. The sensor typically has an IR LED & an IR photodiode, and combining these two gives way to a photo-coupler or optocoupler.
The IR LED is basically a transmitter emitting IR radiations; it looks similar to a standard LED. And since the radiation it generates is not cannot be seen by the human eye; the radiation is detected by infrared receivers which are available in photodiodes form.
The infrared photodiode responds to the infrared light generated by the infrared LED. The resistance of photo-diode & the change in output voltage is directly proportional to the infrared light. However, it is imperative to remember that IR photodiodes are not the same as usual photodiodes as they detect only IR radiation.
After the infrared transmitter has produced an emission, it arrives at the object & some of the emission bounces or reflects back towards the infrared receiver. Based on the intensity of the response, the sensor output is decided by the IR receiver.
Applications of infrared sensors
Today, IR sensors are used in many areas, all of which tap into their myriad applications. For instance, the speed sensor is used to synchronize the speed of multiple motors. The temperature sensor is used for industrial temperature control. Passive infrared sensors, aka PIR sensors, are used in automatic door opening systems, while ultrasonic sensors are used for measuring distances.
Apart from being used in sensor-based projects, IR sensors are used in a wide range of appliances/ electronic devices as mentioned below.
IR Imaging Devices
One of the major applications of IR sensors is IR imaging devices; think thermal imagers, night vision devices, (night-vision cameras), infrared astronomy, etc.
Even though infrared radiation cannot be seen, it is emitted by water, rocks, soil, vegetation, the atmosphere and even human tissue. Thermal infrared detectors can measure these radiations in the IR range and share the temperature distributions of the object/area on an image.
Radiation Thermometers
IR sensors are used in radiation thermometers that are used for measuring the temperature of a body based on its emitted thermal radiation. These thermometers are used mainly due to their ability to measure temperature without direct contact with the object, quicker response times and easy pattern measurements.
Flame Monitors
They are used for detecting the light emitted from the flames and to see how the flames are burning.
Moisture Analyzers
Moisture analyzers have an infrared weighing and heating unit which uses wavelengths absorbed by the moisture to arrive at the levels of moisture in the given sample.
Gas Analyzers
IR sensors are also used in gas analyzers and gas detectors. They are in turn used for process safety improvement, quality studies, efficiency analysis, and emissions monitoring.
The above devices in turn are used in areas such as meteorology, climatology, photo-bio modulation, water/ gas analysis, testing anesthesiology, petroleum exploration and rail safety. Moreover, with PIR-based sensors being used for motion detection, even security alarms and automatic lighting applications have come to reply on IR sensors. Additionally, infrared technology today is used for remote controls and even in fiber-optic cables.
Strengths of infrared sensors
Infrared sensors afford many advantages, which is why they are widely used today. Let us look at the advantanages:
- Less power consumption
A key advantage is that an IR sensor doesn’t take up much power. - Contact-less detection
An IR sensor does not need contact with the object for detection. - No data leakage
With IR sensors, there is no data leakage caused by the ray direction. - Immune to noise
IR sensors are highly immune to noise. - Immune to oxidation and corrosion
These sensors are not affected by oxidation & corrosion. - Low dependence on light
IR sensors can detect motion with equal reliability regardless of the presence or absence of light.
Limitations of infrared sensors
Infrared sensors also come with some disadvantages. Let’s look at them here:
- Line of sight is needed
For smooth functioning of an IR sensor, a line of sight is necessary. - Limited range
IR sensors come with a limited range and hence, cannot be used in all situations. - Vulnerable to climate and surrounding conditions
IR sensors are affected by changes in climate, temperature and humidity. So fog, rain, dust can interfere with its smooth functioning. - Less data transmission rate
Another limitation is that IR sensors do not boast a high transmission rate.
Enhance Your Child's Understanding of Infrared Sensors
For those intrigued by the workings of an infrared sensor and wishing to further explore the realms of technology, Coding Classes for Kids at YoungWonks provide an ideal starting point. Our curriculum is designed to enrich young minds with practical knowledge and hands-on experience in tech fields. Specifically, our Python Coding Classes for Kids serve as a fantastic resource for those eager to dip their toes into the world of programming. Further, for enthusiasts interested in hardware programming and interactive projects, our Raspberry Pi, Arduino and Game Development Coding Classes offer an in-depth understanding and applications of infrared sensors in real-world scenarios. Embark on a learning adventure with YoungWonks and unveil the magic of technology.
*Contributors: Written by Vidya Prabhu; Lead image by: Abhishek Aggarwal