Jul 29, 2021 By Team YoungWonks *
With the advent of blockchain technology, smart contracts is a term that has come to be commonly used. What then is a smart contract? Read our blog to know more. But before we delve into this, it would be a good idea to get acquainted with blockchain technology since the two are inter-related. Here's our blog on blockchain technology: https://www.youngwonks.com/blog/What-is-Blockchain-Technology.
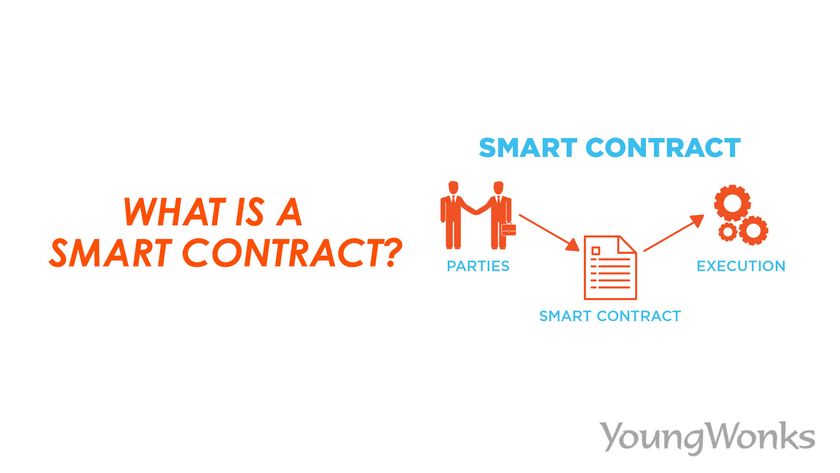
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is essentially a computer program or a transaction protocol created to automatically execute, control or document legally relevant events and actions as per the terms of a contract or an agreement. The main goals of smart contracts are lesser dependence on intermediators, arbitrations and cutting down of enforcement costs plus fraud losses. Basically, smart contracts help one exchange money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent, conflict-free way while avoiding the services of a middleman.
In a sense, vending machines would be the oldest technology similar to smart contract implementation. Or you can think of smart contracts as a vending machine. Typically, one goes to a lawyer or a notary, pays them, and waits for the document. With smart contracts, you simply put a bitcoin into the vending machine (i.e. ledger), and your escrow or driver’s license is deposited into your account.
So yes, the biggest reason behind using smart contracts is the fact that they allow for trusted transactions and agreements to be carried out among varied anonymous parties without the need for a central authority, legal system, or external enforcement mechanism.
Origins of Smart Contracts
In 1994, cryptographer and computer scientist Nick Szabo got the idea of recording contracts in the form of computer code. The contracts would have a built-in function of getting activated automatically upon certain conditions being met. This idea meant doing away with trusted third-party companies such as banks, brokers, or a government, in turn making transactions that much smoother and faster.
The goal, in Szabo’s words, was to bring together the practices of contract law and practice with the design element as part of electronic commerce protocols between strangers on the Internet. Not only did he wish to extend the functionality of electronic transaction methods (think POS aka point of sale) to the digital realm, but he also suggested the execution of a contract for synthetic assets, such as derivatives and bonds.
Today, smart contracts are a major feature of cryptocurrency. In fact, since the launch of the Ethereum blockchain in 2015, the term smart contract has been more specifically used to refer to the general purpose computation that takes place on a blockchain or distributed ledger.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
As mentioned earlier, a smart contract is an agreement between two people in the form of computer code. Such contracts - like any other contract - specify the terms of the agreement between the parties. The first step entails finalizing the terms of the contract which are then translated into code.
Once this code representing the terms of agreement is created, it is stored in a blockchain. Now we know from our previous blog on blockchain technology that the blockchain refers to a chain of blocks that are connected to each other using cryptography and are managed by a peer-to-peer network of computers / users who collectively follow the protocol for communication and validating new blocks. This means that as soon as the block is created, it is sent to everyone in the network to be validated and stored. Upon validation by consensus, these contracts - stored as they are in blocks on the blockchain network - become unalterable.
And because blockchains are decentralized systems - each record is maintained not just in one place but across a wide network of computers - the transactions laid down in a smart contract are automatically processed by the blockchain platform as and when the conditions mentioned are fulfilled and without any third party.
Advantages of Smart Contracts
There are many advantages to using smart contracts instead of traditional agreements. Let’s look at them one by one.
a. Accuracy: A major requirement of a smart contract is to record all terms and conditions in the tiniest detail. And the best part is that one doesn’t have to go through reams of paper at a later stage, since the terms and conditions have already been fleshed out in an elaborate fashion in the automated contract.
b. Transparency and No Room for Misinterpretation: With the terms and conditions of these contracts fully visible and accessible to the relevant parties, there is clear communication between them.
c. Speed: Given that these contracts run on code on the blockchain, transactions can be carried out very quickly. Plus there is no need to process documents manually thus resulting in increased efficiency.
d. Security: Smart contracts rely on the highest level of data encryption currently available, which is the same as that used by modern crypto-currencies. So the parties can be assured that their contracts are safely stored.
e. Paper-Free and Environment-Friendly: With smart contracts, there is no need for thick wads of paper and big files. Environment conscious businesses can now do their bit by switching to these contracts.
f. Storage & Backup: Unlike traditional contracts which take up physical space and can be lost over time, these contracts get permanently stored on the blockchain for future records.
g. Savings: With the middlemen cut out, automated contracts keep the transaction between the concerned parties, helping them save on paying off the third party (think lawyers, witnesses, banks and other intermediaries).
Overall, smart contracts afford greater transparency, autonomy and security, thus inspiring absolute confidence with their smooth execution.
Applications of Smart Contracts
Due to the myriad advantages of using smart contracts, they can be relied upon in several areas today. Shared below are the different use cases that can gain from the use of smart contracts.
Trade and finance: Approval automation being a key feature of smart contracts, they help workflows become smoother even as clearances take up less labor and thus time.
Supply chain management: Supply chains can be managed much better with blockchain-based smart contracts. For starters, Internet of Things devices could be used throughout the chain to record every step thus keeping track of each item and its whereabouts at a given time. Even in large warehouses, these smart contracts could help managers see real-time stock levels and the time it takes for products to move along the supply chain, in turn helping them improve delivery times. Moreover, smart contracts could be used to even initiate automatic reorders and payment for orders already received.
Product development: Similarly, smart contracts can be used to keep a ledger recording the stages of product development. Two parties would sign the contract as per certain terms and the product development stages would be recorded in the smart contract. So in cases of parties agreeing to split payments, the payments would be made upon reaching the milestones shared in the contract and all of this would be done without compromising on the security of the sensitive information (think intellectual properties owned by big and small companies).
Peer-to-peer transactions: Smart contracts can be used for peer-to-peer transactions (think any business transaction between two parties). And it is this use that paved the way for the creation of the Ethereum blockchain and other such companies. Users from different fields can use these platforms to create mutual agreements. These contracts stay active till the agreed conditions are met. Once this happens, the remaining portion of the agreement is fulfilled. This portion of the agreement is typically the transfer of money (and cryptocurrencies) but it can also refer to securing the services of development teams.
Insurance: In addition to supporting the initial insurance policy, smart contracts can help improve insurance companies with claim processing - be it carrying out error checks or determining payout amounts as per a set of criteria (that factors in the policy held by the individual or organization), all in reduced time, with greater accuracy and lower costs.
In the long run, smart contracts could be used with Internet of Things enabled vehicles to facilitate pay-as-you-go insurance policies and the immediate activation of claims after an accident. Processing information such as driver licenses, driving records, accident reports, and policy details could be carried out in shorter periods as well.
Real estate dealings: Smart contracts can be used to record property ownership and rentals/ leases, doing away with the need for lawyers and housing brokers. Even mortgage transactions can be carried out faster and in a more efficient fashion with such contracts. There would also be greater transparency between both parties as the change of ownership would be reflected only after unique key code authorization on behalf of the original owner, thus making the whole process more secure and reducing instances of fraud.
In fact, such contracts can be used to record ownership and rentals of other commodities too - think jewelry, phones, watches, etc along with buildings and land.
Healthcare: Today, millions of patient medical records are being stored in the world‘s healthcare computer systems. If this information is converted into smart contracts, it will come to enjoy the benefits afforded by blockchain technology: think entire databases securely encrypted and kept and accessed only by those who have the private key. Moreover, smart contracts can also be used for issuing prescriptions, storing receipts, general stock management, storing test results, and so on.
Medical research: Using smart contracts, highly sensitive data such as patient records could be transferred in a secure fashion between departments/research centers. Similarly, medical research companies could use smart contracts to store test results and new drug formulas.
Voting: Voting fraud can be effectively dealt with using smart contracts; they can be used to validate a voter‘s identity and record their vote. Given the fact that the blocks within a blockchain cannot be altered once they have been recorded, manipulation of this record would not be possible.
Solving macroeconomic problems: Smart contracts can also be used to address macro-economic problems, especially related to distribution. Complex problems such as fractional ownership - for instance, many farmers owning one tractor to bring down the costs per farmer or even equitable distribution of power across an area - can be dealt with smart contracts.
Notwithstanding the many advantages to using smart contracts, it is important to note here that smart contracts are not the same as smart legal contracts. The latter alludes to a traditional natural language legally-binding agreement which has certain terms expressed and implemented in machine-readable code.
Also, a smart contract does not necessarily have to be a valid binding agreement at law. Some legal academics even state that smart contracts are not legal agreements, instead calling them means of automation of payment obligations and means of transfer of tokens or cryptocurrencies. Plus, other scholars have emphasized that the imperative or declarative nature of programming languages can affect the legal validity of smart contracts.
That said, efforts are on to legalize them. In 2017, by implementing the Decree on Development of Digital Economy, Belarus became the first-ever country to legalize smart contracts.
Understanding Smart Contracts with YoungWonks
In the evolving world of blockchain and digital transactions, smart contracts stand as a pivotal innovation ensuring security and trust without the need for intermediaries. By enrolling in Coding Classes for Kids at YoungWonks, students can start their journey into understanding the fundamentals behind these autonomous, self-executing contracts coded into blockchain. For those particularly interested in the programming aspects that make smart contracts possible, our Python Coding Classes for Kids offer a great starting point, given Python's significant role in blockchain technology. Additionally, enthusiasts wishing to explore the hardware side or the creation of interactive technology projects can benefit from our Raspberry Pi, Arduino and Game Development Coding Classes. Here, students gain hands-on experience which is crucial for understanding the operational environments where smart contracts can be employed.
*Contributors: Written by Vidya Prabhu; Lead image by: Abhishek Aggarwal