Sep 02, 2021 By Team YoungWonks *
What is OpenCV? Those in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) certainly have to learn more about it. In this blog, we shall look at what OpenCV is, how it works and where it is used today. And before we delve further into what OpenCV means, let us look at the meaning of the term computer visions and image processing.
What is Computer Vision?
Computer vision refers to a process which enables one to understand images and videos, how they are stored and how they can be manipulated and data retrieved from them. More often than not, computer vision forms the basis for AI. Today, it has an important role to play in self-driving cars, robotics and even in photo correction apps.
What is Image Processing?
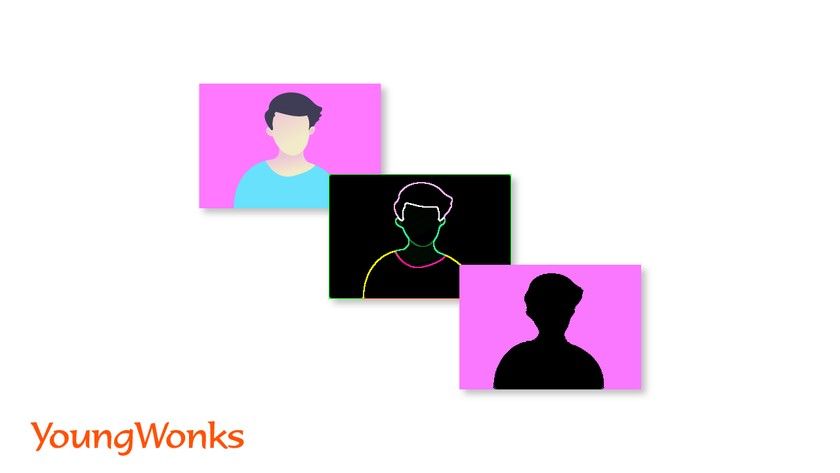
Image processing refers to the analysis and manipulation of a digitized image, especially in order to improve its quality. In other words, it involves operations performed on images so as to get their enhanced versions or to glean/ extract some useful information from them. Typically such operations comprise the steps of importing the image, analyzing and manipulating it and getting the output that is typically a modified image or a report based on the image analysis.
As a result, image processing helps with tasks such as reading and writing images, detection of faces and its features, detection of shapes such as circles, squares, rectangles in an image (for instance, detection of coins in images), text recognition in images (reading vehicle number plates), changing image quality and colours / filters (think apps like Instagram) and developing Augmented Reality functionality or apps.
This brings us now to OpenCV, the focus of this blog post. So what is OpenCV?
What is OpenCV?
OpenCV stands for Open Source Computer Vision. To put it simply, it is a library used for image processing. In fact, it is a huge open-source library used for computer vision applications, in areas powered by Artificial Intelligence or Machine Learning algorithms, and for completing tasks that need image processing. As a result, it assumes significance today in real-time operations in today’s systems. Using OpenCV, one can process images and videos to identify objects, faces, or even the handwriting of a human.
Originally developed by Intel, OpenCV was later supported by Willow Garage then Itseez, in turn later acquired by Intel. The first OpenCV version was 1.0. Released under a BSD license, this cross-platform library is free for both academic and commercial use under the open-source Apache 2 License. It has C++, C, Python, Java and MATLAB (a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language that offers a good numeric computing environment) interfaces and the API for these interfaces can be found in the online documentation. OpenCV also supports Windows, Linux, Mac OS, iOS and Android. Initially, the main aim of creating OpenCV was real-time applications for computational efficiency. Since 2011, OpenCV also offers GPU acceleration for real-time operations. Upon integration with other libraries, such as NumPy, Python can process the OpenCV array structure for analysis. Identifying image patterns and its several features needs use of vector space and carrying out mathematical operations on these features.
To learn the basics of Python Image Processing using OpenCV refer to our blog on the link given below:
https://www.youngwonks.com/blog/Getting-started-with-Python-Image-Processing-using-OpenCV
Applications of OpenCV
There are lots of applications which rely on the use of the Open Source Computer Vision library. Let’s look at them.
Face detection / face recognition/ facial recognition system
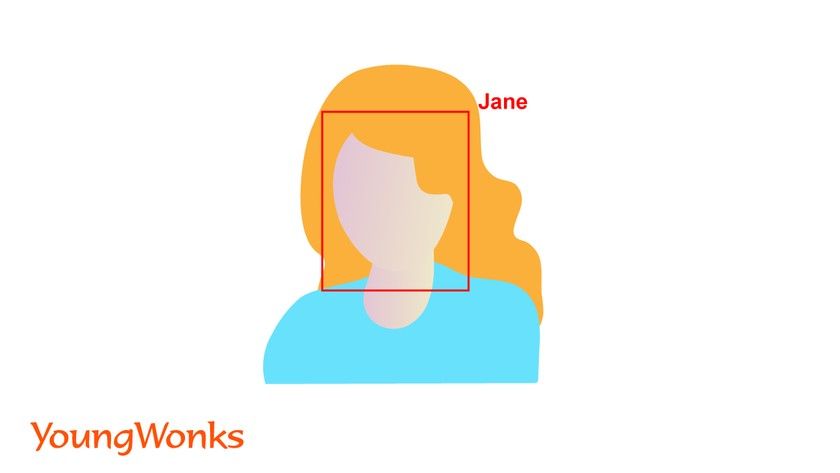
A facial recognition system is a technology that can match a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. It is used to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image.
Egomotion estimation
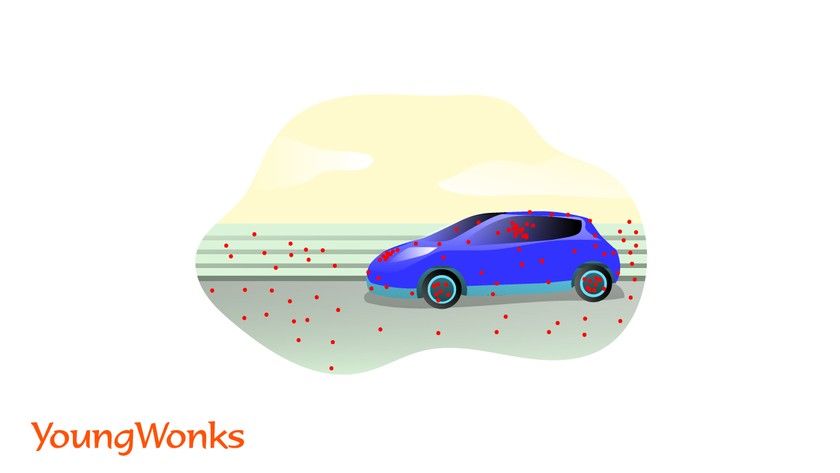
Egomotion refers to the 3D motion of a camera within an environment. In the context of computer vision, egomotion deals with estimating a camera’s motion relative to a rigid scene. An example of egomotion estimation would be estimating a car’s moving position with respect to lines on the road or street signs being seen from the car itself. The estimation of egomotion is important in autonomous robot navigation applications.
Gesture recognition
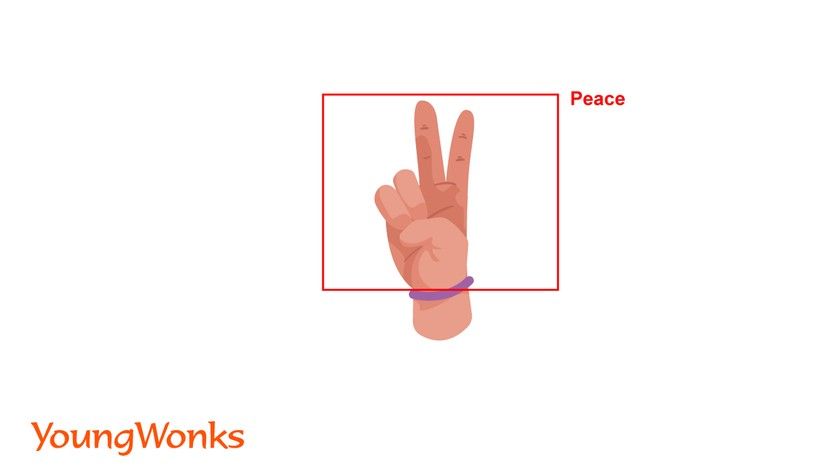
A subdiscipline of computer vision, gesture recognition works with the goal of interpreting human gestures via mathematical algorithms. Gestures can stem from any bodily motion or state but commonly originate from the face or hand.
Human–computer interaction (HCI)
Human-computer interaction (HCI) is a field of research in the design and the use of computer technology, which studies in detail the interfaces between people (users) and computers. HCI researchers focus on the ways in which humans interact with computers and design technologies allowing humans to interact with computers in novel ways.
Mobile robotics
A mobile robot is a robot that can move in its surroundings. Thus mobile robotics is a subfield of robotics and information engineering.
Motion understanding
As the term suggests, motion understanding refers to understanding, interpreting and overall analysing the motion of objects in certain environments, such that we are able to better predict their movements and and interact better with them.
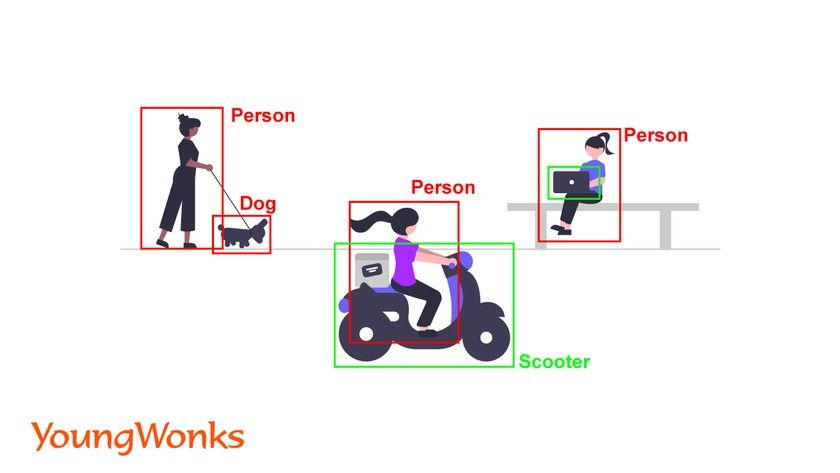
Object detection
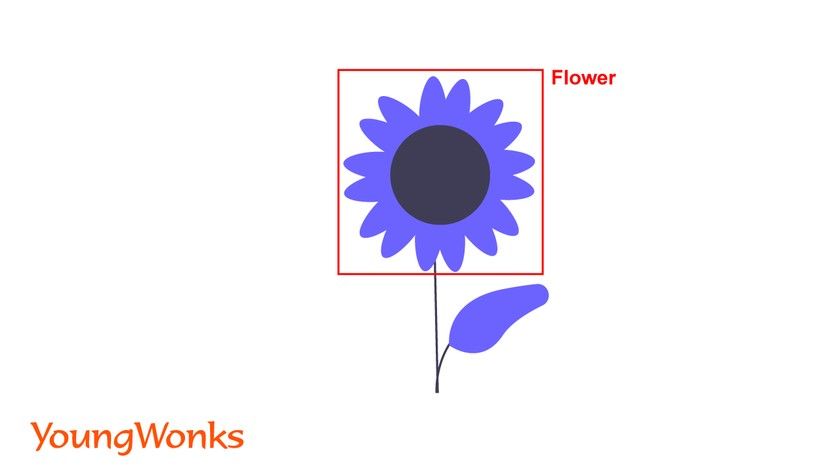
Object detection is a computer technology related to computer vision and image processing that focuses on identifying instances of semantic objects of a certain class (such as humans, buildings, or cars) in digital images and videos.
Image segmentation and recognition
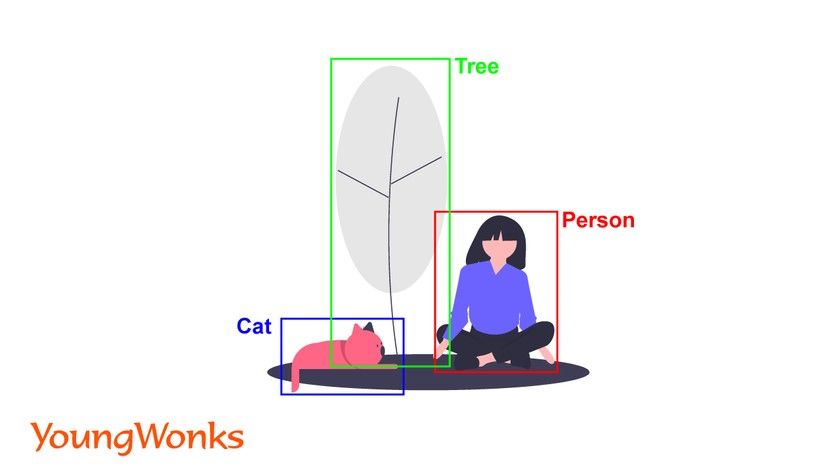
In digital image processing and computer vision, image segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple segments (sets of pixels, also known as image objects). The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze.
Stereopsis stereo vision
Here stereopsis refers to the perception of depth and 3-dimensional structure formed on the basis of visual information gained from two cameras.
Structure from motion (SFM)
Structure from motion (SFM) is a photogrammetric range imaging technique for estimating three-dimensional structures from two-dimensional image sequences that can be combined with local motion signals. It is studied in the fields of computer vision and visual perception.
Motion tracking
Also known as video tracking, motion tracking is the process of locating a moving object (or multiple objects) over time using a camera.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) is basically an interactive experience of a real-world environment where the objects in the real world get enhanced by computer-generated perceptual information, often across several sensory faculties, be it visual, auditory, haptic, somatosensory and olfactory.
Ideal Use Cases for OpenCV library
Thanks to the above applications, there are many ideal use cases for OpenCV including (and not limited to):
1. Automated inspection and surveillance
2. Tracking the number of people in a place (for instance, the foot traffic in a mall)
3. Vehicle count on highways along with their speeds
4. Street view image stitching
5. Defect detection in manufacturing processes
6. Interactive art installations
7. Video/image search and retrieval
8. Object recognition
9. TV Channels advertisement recognition
10. Robot and driver-less car navigation and control
11. Analyzing medical images
12. Figuring out 3D structure from motion captured in videos/ films
Advantages of using OpenCV
Ease of use: OpenCV is easy and simple to learn
Availability of many tutorials: The fact that there are lots of tutorials available is a big plus as one can access many learning resources.
Compatibility with leading coding languages: OpenCV works with almost all the leading programming languages today, including Python, C++ and Java.
Free to use: Undoubtedly, a big plus is the fact that it is open source and hence free to use.
Exploring Further with YoungWonks
For those inspired by the endless possibilities of OpenCV and eager to leap into the world of programming, Coding Classes for Kids at YoungWonks offer a perfect launching pad. Not only do we lay a strong foundation in programming fundamentals, but we also offer specialized Python Coding Classes for Kids that equip students with the skills to harness the power of libraries like OpenCV for projects ranging from simple pattern recognition to complex image manipulation. Furthermore, our Machine Learning and AI Classes for Kids are designed to introduce young minds to the fascinating world of AI, enabling them to apply their Python skills in creating smart applications that can learn, predict, and act.
*Contributors: Written by Vidya Prabhu; Lead image by: Abhishek Aggarwal