Nov 12, 2022 By Team YoungWonks *
What are Python text files?
Text files are human readable files which contains characters and has no specific styling.
Python has inbuilt functions to read, write and create text files. Python program can be used to access the text files stored in main memory using file handling. It can read two types of files i.e. binary files and text files. Text files have end line character by default at the end of each line. These text files are txt files. In binary files data is stored in binary language containing 1’s and 0‘s which can be read using the binary mode.
Read Text Files
Files can be opened in various modes such as read, write, read and write and append. In this Python tutorial, we'll go over all of the methods available in Python to read text files. We can read txt files based on different file access modes. The three important modes are read, write and append mode.

1. Read only mode
This is the mode where a text file is opened for reading only. We can access the content of the file using this mode.
In order to read an existing file we use the function given below:
Syntax:
file object = open (‘filename/filepath’, ‘r’)
Here, a variable is created to open file in the read mode which is represented using ‘r’. Either the file name or the path of the file can be used to access the file from the local system.
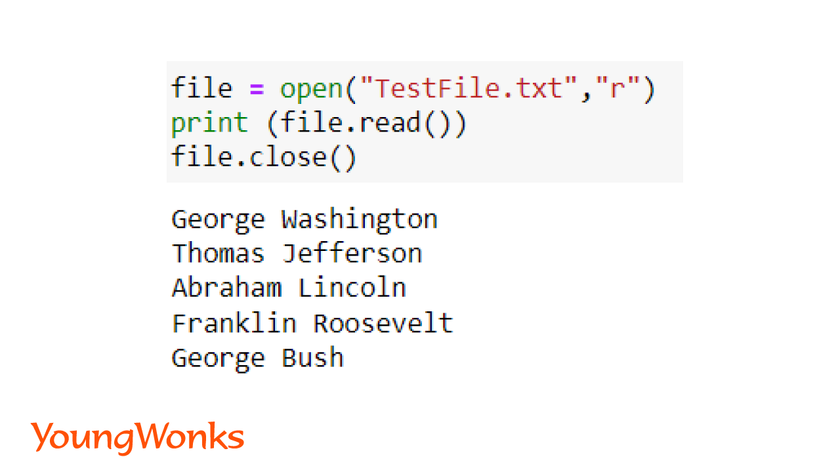
a. We can read the entire file at one go. We can also get the whole file’s data and display it in the Python output window.
Syntax:
f = open (‘filename‘, ‘r’)
f.read()
f.close()
After performing the operations it is important to close files at the end of the file.
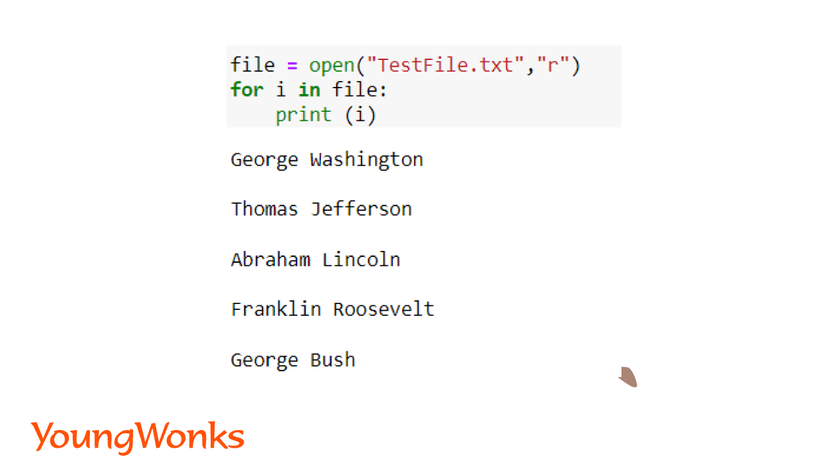
b. We can read the content of the whole file line by line as well. There are two ways to read the each line of the file.
- f.readline() is used to read a single line in a text file. Each line can be read from a file. If we want to read multiple lines one by one, we can use the readline function multiple times.
- f.readlines() is used to read the complete file and it returns a list of strings. We can also iterate through the text file in order to read each line of a file.
- We make use of a for loop or a while loop to read line by line.

Syntax:
for line in file:
print (line)
Here, line will print each line from the text file. In a text file, there is a newline character at the end of each line. In order to use the data from a text file using a Python file, we can remove the new line character using the strip function in Python.
In the example given below you can check the use of the strip command.
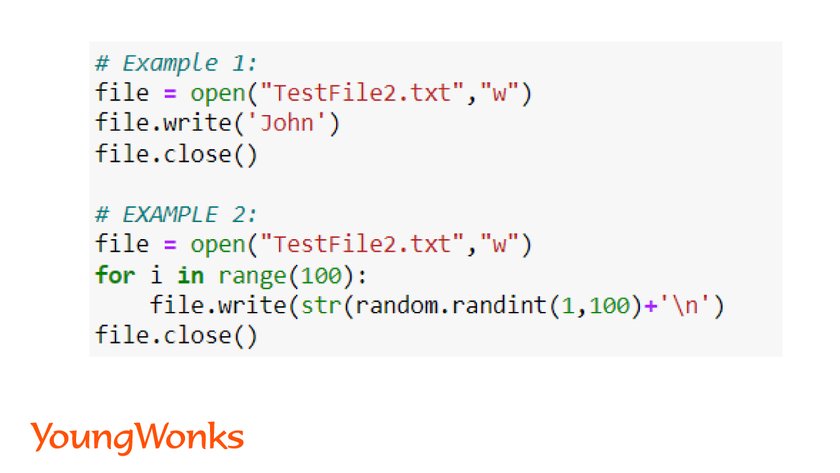
2. Write mode:
In this mode if a file exits its over-written else it creates a new file and information is written into it.
Syntax:
f = open (‘filename‘, ‘w’)
- f.write() command is used to write into a text file. We also add \n if we want the data to be written in different lines.
3. Read and write mode
In this mode we can read and write in a file simultaneously.
Syntax:
f = open (‘filename‘, ‘r+’)
4. Append mode
We can add new information into a text file. In this mode, the earlier information in an existing file is not over-written.
Syntax:
f = open (‘filename‘, ‘a’)

5. Append and read mode
We can read contents of a file and append information in the same text file using this mode.
Syntax:
f = open (‘filename‘, ‘a+’)
Expanding Your Child's Coding Skills
For parents looking to further nurture their child's interest in coding, particularly in Python, resources like Coding Classes for Kids provide a comprehensive platform to start this exciting journey. Specifically, through Python Coding Classes for Kids, young learners can grasp the fundamentals and advanced concepts of Python in a fun and engaging environment. Additionally, for those interested in exploring beyond Python, Raspberry Pi, Arduino and Game Development Coding Classes offer a unique opportunity to dive into hardware programming and game development, equipping them with a versatile skill set in the vast domain of coding.
*Contributors: Written by Aayushi Jayaswal; Lead image by Shivendra Singh

