Sep 04, 2022 By Team YoungWonks *
What is a list?
A list is a collection of items. A list is a data structure in programming that is used to store data. The data can take any form. A list is present in all programming languages; however, it is referred to by a different word in each one. In C++ and Java, for example, it is referred to as arrays. In Python programming, it is known as a list. We will learn Python lists in depth by manipulating lists in this Python tutorial.
How do we use a list in Python Programming?
It is formed with square brackets and can contain any data type, such as strings (str), integers (int), floats, and booleans (bool). A comma is used between each item to separate it. They are mutable in nature, which means that direct changes can be made to a list. Changes to the list can be made using the built-in functions.
Python List Methods
Below is the list of Python commands that can be used to directly manipulate a list. These commands are often referred to as list functions or, more accurately, list methods.
1. Create a list
At first, we will learn how to create an empty list.
Syntax: list = [ ]
To create a list of items, items name are added into the list one after the other.
Syntax: list = [ item1, item2, item3 ]

2. Count number of items in a list
To count how many items are present in the list, we use the length function to find the length of the list.
Syntax: len(list)

3. Add Items into a list
We can add items into a list using two ways.
a. Using the name of the item: This method adds an item at the end of the list.
Syntax: list.append(item name)

b. Using index: This method is used to add the new item at a specific position.
Syntax: list.insert(index, item name)
index = position of the item; start value = 0 (index of first element)

4. Remove Items from a list
We can remove items from a list using two ways.
a. Using the name of the item:
Syntax: list.remove(item name)

b. Using index: This method is used to remove an item from a specific position.
Syntax: list.pop(index)
The default value is -1. -1 is the index of the last item there it removes the last item from the list.
This method has a return value. Similarly, to remove the first item you can specify the index as 0.

5. Get items from a list
We can use index to get list items.
Syntax: list[index of the element]
6. Find position of an Item
This method returns the index of the element.
Syntax: list.index(item name)
Let us look into the examples of the last two methods given below:

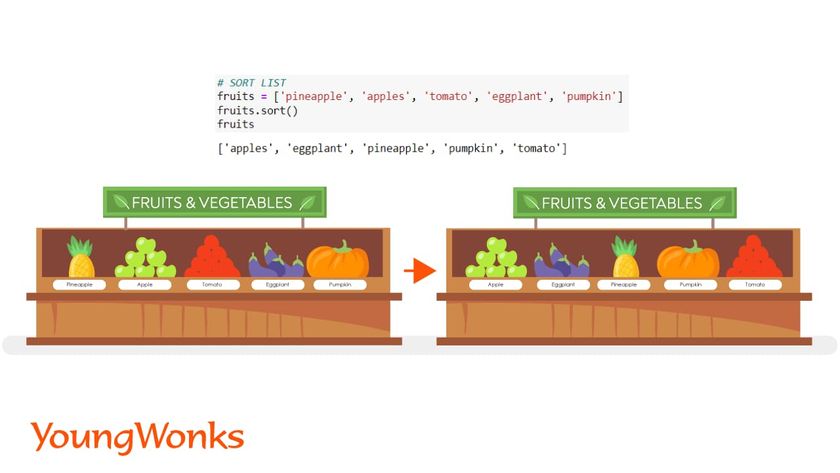
7. Sort the list
Using this method, the sorted list returns strings into alphabetical order and a list of numbers in ascending order.
Syntax: list.sort( )
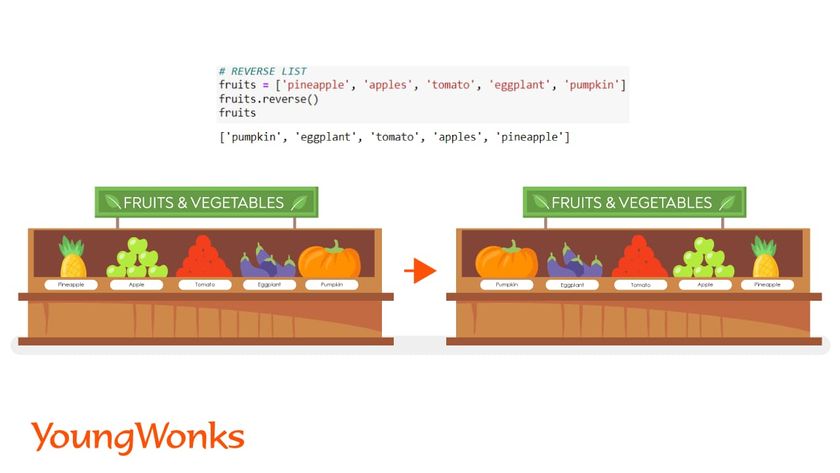
8. Reverse the list
In this method, the elements of the list is reversed.
Syntax: list.reverse()
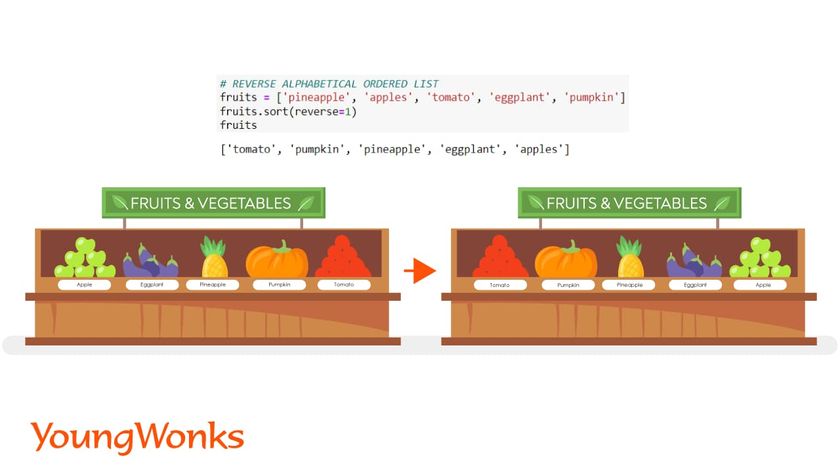
To convert the list into reverse alphabetical order or descending order:
Syntax: list.sort (reverse=1)
Here, the parameter reverses the list after sorting it.
9. Replace list items
We make use of index to replace the items of a list.
Syntax: list[index of the element] = new item

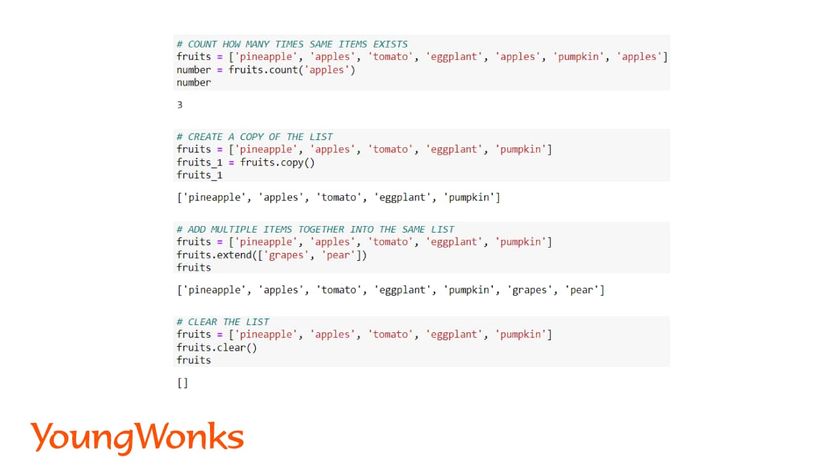
10. Count the number of specific items
This method returns of the count of the item in the list.
Syntax: list.count(item name)
11. Make a copy of the list
Lists can be copied to create its duplicate and use it.
Syntax: new list = list.copy()
12. Add Multiple items using one-step
Here, we can add multiple items in the form of a list and the extend method is used to add all of the items into the original list.
Syntax: list.extend([item1, item2])
13. Empty the list
This function removes all the items of the list.
Syntax: list.clear()
Now, let us look into the examples for the above four methods:
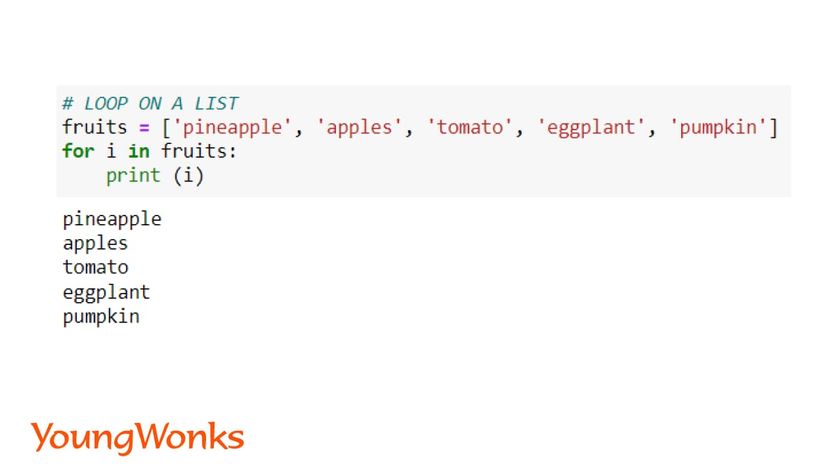
14. Get each item of the list
Lists are iterable i.e. we can make use of a loop on it.
Syntax:
for i in list:
print (i)
Here, the for loop variable stores each item of the list one by one.
15. Maximum and Minimum number from the list.
Syntax: max(list); min(list)
This returns the maximum and minimum number from a list of numbers.
16. Random module on lists
We can use a few random module functions on a python list. This can perform specific actions on the list such as picking random item, jumble up the items of a list.
a. Pick random item from a list:
Syntax: random.choice(list)
b. Pick random item from a list as a list:
Syntax: random.sample(list, 1)
Here, the second parameter is to specify how many items we require.
c. Randomly jumble the items of a list.
Syntax: random.shuffle(list)

17. String into list
To convert strings into a list, we can use a few list methods. Certain actions, such as rearranging the characters of a string, are not possible with the string method. As a result, the list is a workaround for performing such operations.
a. List of words: Convert a string into list of words.
Syntax: list.split(‘character’)
Here, the parameter is given to convert a string into list of word. A string can be split from any character.
b. List of letters: Convert a string into list of letters.
Syntax: list(listvar)
Here, list is the keyword for this method, list variable is added as the parameter.

All of the functions listed above enable the user to carry out the necessary actions. In Python, however, there is another type of list known as tuples. These are immutable in nature, which means that changes cannot be made directly in them using the methods listed above. They are formed with parenthesis, and items are separated by commas.
Syntax: tuple = (item1, item2, item3)

Now that we have learnt all the Python list methods. Let us look into list comprehension. This is a shorter way to create a new list of items or create a new list from existing list.
Syntax: list = [ i for i in range() if (condition)]

Summary
In this blog, we learned about all of the built-in Python list methods, as well as how to use the random module on a list and convert a string into a list. You can now incorporate these into your programmes. In a future blog, we will go over the Python string methods in depth.
Enhancing Your Child's Coding Skills
To further elevate your child's coding skills and understanding of Python list methods, consider enrolling them in specialized coding classes. At Coding Classes for Kids, we offer a comprehensive curriculum tailored to young learners. For those particularly interested in Python, our Python Coding Classes for Kids provide an excellent foundation in Python programming, enabling students to effectively manipulate list methods and more. Additionally, for kids fascinated by hardware, our Raspberry Pi, Arduino and Game Development Coding Classes open up a world of possibilities in physical computing and game development, further enhancing their programming toolkit.
*Contributors: Written by Aayushi Jayaswal; Lead image by Shivendra Singh

